Population Growth Trends: A Global Perspective on Dwindling Numbers
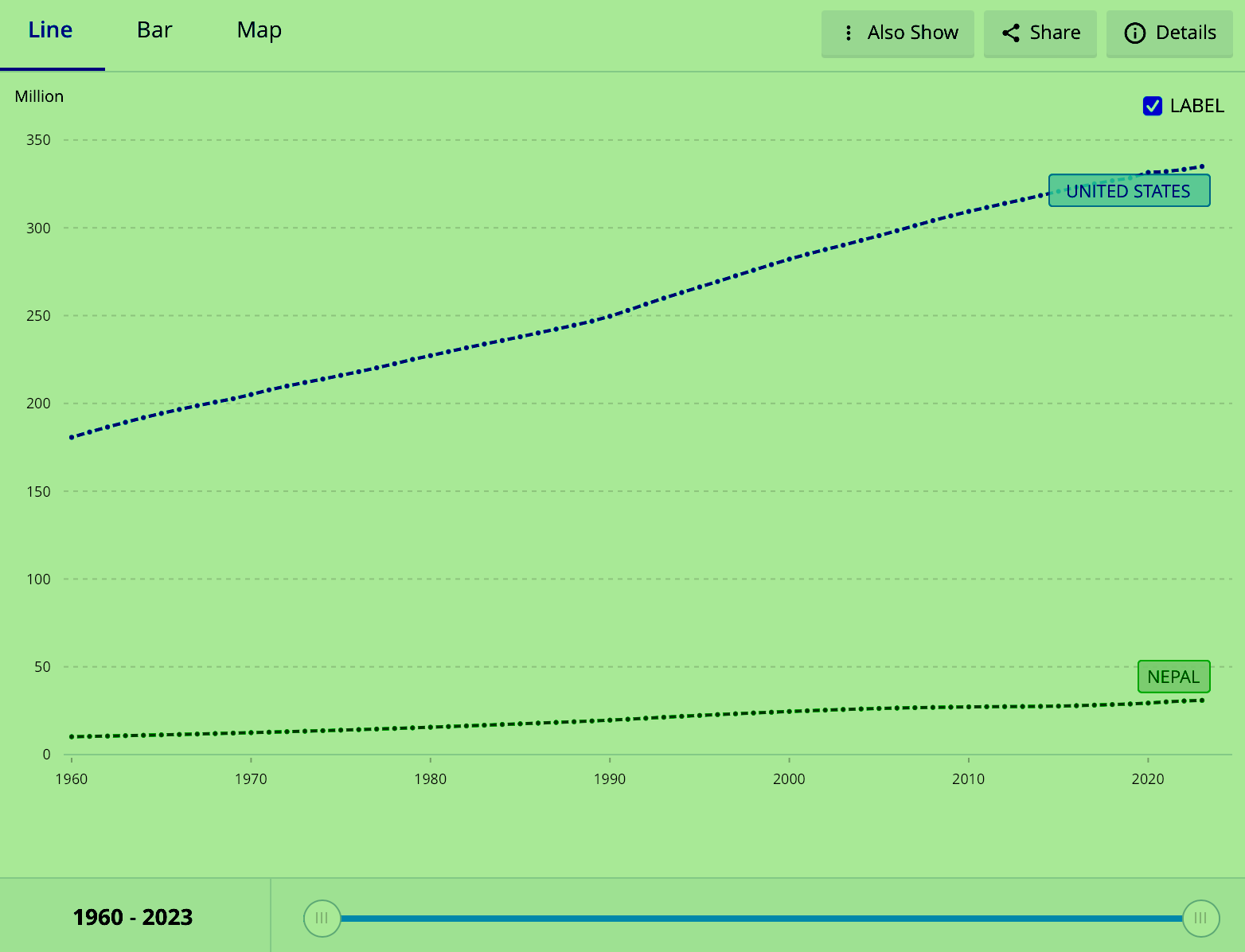
Population growth has long been a cornerstone of economic and social development, providing the labor force necessary for progress and ensuring the vitality of nations. However, recent trends indicate that many countries, including the United States and Nepal, are experiencing stagnation or decline in their population growth rates, raising concerns about the potential for future economic stagnation, social upheaval, and global imbalance. This article explores the causes, effects, and future consequences of dwindling population growth on a global scale.
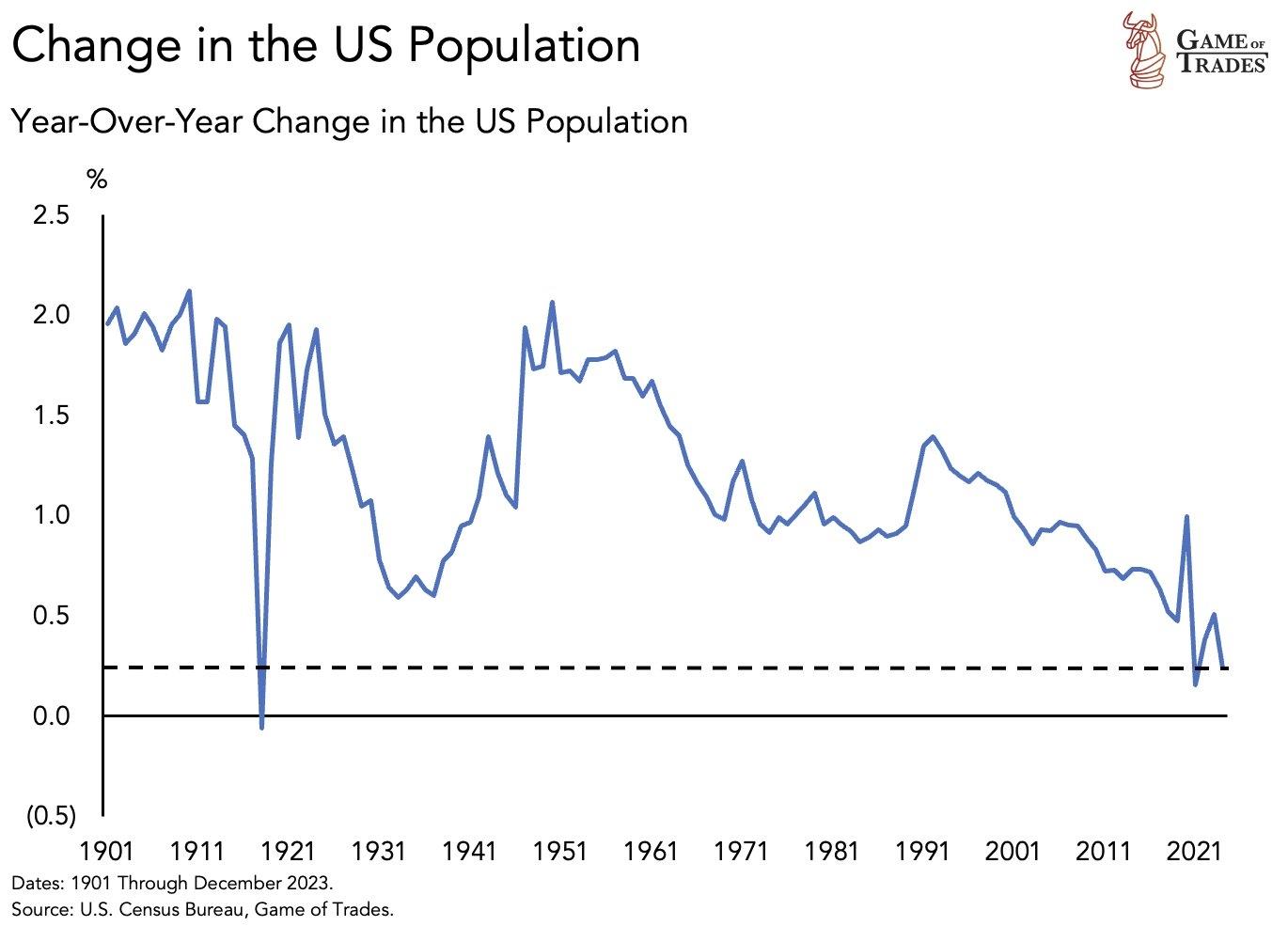
Causes of Declining Population Growth
1. Falling Fertility Rates
One of the primary causes of declining population growth is the significant drop in fertility rates. In many developed countries, including the US, fertility rates have fallen below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman. This decline can be attributed to a variety of factors:
- Economic Pressures: The high cost of living, housing, and child-rearing expenses discourage many from having larger families.
- Career and Education Priorities: Increasing numbers of women pursuing higher education and careers often delay marriage and childbirth, reducing the number of children born.
- Urbanization: Urban living often correlates with lower fertility rates as city life can be more expensive and less conducive to larger families.
2. Aging Populations
Many countries are experiencing an aging population due to increased life expectancy and declining birth rates. The demographic shift towards an older population puts additional pressure on social services and pension systems, as fewer working-age individuals are available to support an expanding elderly population.
3. Migration Patterns
While migration can temporarily boost population numbers, it is not always sufficient to offset natural decline. Many countries with high emigration rates suffer from a net loss of population, further exacerbating the decline. Conversely, countries with high immigration rates may face integration challenges and cultural shifts.
4. Economic Uncertainty and Social Instability
Economic instability and social unrest can also contribute to declining birth rates. In regions facing severe economic downturns, such as parts of Europe and Latin America, young people may delay or forgo starting families due to financial insecurity.
Effects of Declining Population Growth
1. Economic Implications
A shrinking population can lead to several economic challenges:
- Labor Shortages: Fewer people entering the workforce can result in labor shortages, potentially stifling economic growth and innovation.
- Reduced Consumer Demand: A declining population may lead to decreased consumer demand for goods and services, affecting businesses and potentially leading to economic contraction.
- Increased Tax Burden: With a smaller working-age population, the tax burden on the remaining workers may increase to support social services and pensions for the elderly.
2. Social and Cultural Impact
Declining population growth can also have profound social and cultural implications:
- Changing Social Structures: As populations age, traditional family structures may evolve, potentially leading to a rise in single-person households and altered caregiving dynamics.
- Cultural Shifts: Countries with declining populations may experience cultural shifts as they adapt to new demographic realities, including changes in community dynamics and social cohesion.
3. Global Imbalances
On a global scale, declining population growth can lead to:
- Regional Disparities: While some regions may experience population decline, others may continue to grow, potentially leading to geopolitical tensions and economic imbalances.
- Resource Distribution: Changes in population distribution can impact global resource allocation, affecting everything from food supplies to energy demands.
Future Consequences and Adverse Impacts
1. Economic Stagnation
Continued population decline could lead to long-term economic stagnation. Countries with shrinking populations may struggle to maintain economic growth and development, potentially facing prolonged recessions and reduced global influence.
2. Sustainability Challenges
An aging population with fewer younger individuals to support them poses challenges for sustainability. Pension systems, healthcare services, and social safety nets may come under strain, necessitating major policy reforms and adjustments.
3. Innovation and Competitiveness
With fewer young people entering the workforce, innovation and competitiveness may suffer. Young people are often at the forefront of technological advancements and entrepreneurial ventures, and a shrinking youth demographic could stifle progress in these areas.
4. Global Power Shifts
As different regions experience varying rates of population growth, global power dynamics could shift. Countries with growing populations may gain economic and political leverage, while those with declining numbers may lose influence on the world stage.
Conclusion
The trend of dwindling population growth presents a complex and multifaceted challenge with far-reaching implications. Addressing this issue requires a nuanced understanding of its causes and effects, as well as innovative solutions to mitigate its impacts. Policymakers, businesses, and individuals must work collaboratively to navigate the consequences of a changing demographic landscape, ensuring that future generations inherit a world capable of sustaining growth, stability, and prosperity. As the global population continues to evolve, it is crucial to embrace adaptable strategies and forward-thinking approaches to address the pressing challenges and seize the opportunities presented by this demographic shift.
- चाडपर्वहरू
- धर्म र संस्कृति
- संगीत र कला
- कथा र साहित्य
- भोज तथा भतेर
- विज्ञान र प्रविधि
- चलचित्र र नाटक
- ग्याजेट तथा गेम्स
- जनता र राजनीति
- यात्रा तथा गन्तव्य
- जनावर र पक्षीहरू
- स्वास्थ्य र इस्फुर्ती
- प्रकृति तथा संसार
- अटोमोबाइल/उड्डयन
- बजार/व्यापार/लगानी
- ठुल्दाई. बिसेस


